What Is Customer Churn? Understanding Causes and Effective Solutions

Customer churn is a critical metric that every business should understand and monitor closely. Simply put, customer churn refers to the rate at which customers stop doing business with a company over a given period.
Whether you run a SaaS business, an e-commerce store, or a subscription-based service, knowing what customer churn is and how it affects your operations is essential to sustaining growth and profitability.
In industries like software-as-a-service (SaaS) and subscription businesses, customer churn directly impacts monthly recurring revenue (MRR), making it a top priority for management teams.
For e-commerce and professional services, churn influences customer lifetime value and customer acquisition costs, highlighting the importance of maintaining strong customer relationships.
In this article, we'll explore the various facets of customer churn, including its types, how to calculate it, benchmarks, causes, and, most importantly, strategies to reduce customer churn and retain loyal customers.
Types of Customer Churn
Understanding the different types of customer churn is fundamental to managing and reducing it effectively. There are two primary categories:
1. Voluntary Churn (Active Churn)
Voluntary churn occurs when customers intentionally decide to stop using a product or service. This could be due to dissatisfaction with the product, poor customer service, pricing issues, or simply because their needs have changed.
Voluntary churn is often due to customer dissatisfaction, misaligned expectations, or better alternatives. Voluntary churn occurs when customers choose to leave a product or service on their own, making it a critical area for businesses to address.
2. Involuntary Churn (Passive Churn)
Involuntary churn happens when customers leave unintentionally, often due to failed payments, expired credit cards, or administrative errors. This type of churn is common in subscription businesses where recurring revenue depends on uninterrupted billing cycles.
Involuntary churn is typically seen as a mechanical failure rather than a choice by the customer. Managing involuntary churn through proactive payment reminders and dunning management can significantly reduce customer attrition.
Voluntary churn, on the other hand, is often more easily addressed through proactive customer success interventions.
3. Revenue Churn vs. Customer Churn
It is also important to distinguish between customer churn and revenue churn. Customer churn measures the number or percentage of customers lost, while revenue churn focuses on the lost revenue from those customers.
For example, losing a high-paying customer impacts revenue churn more than losing several low-value customers. Tracking both metrics provides a clearer picture of how churn affects the business financially.
How to Calculate Customer Churn Rate
Calculating customer churn rate accurately is vital for assessing business health and forecasting future revenue.
Basic Customer Churn Rate Formula
The standard formula to calculate customer churn rate is:

For example, if you start the month with 1,000 customers and lose 50 by the end, your monthly churn rate is (50/1000) × 100 = 5%.
Revenue Churn Rate Formula
Revenue churn rate is calculated as:
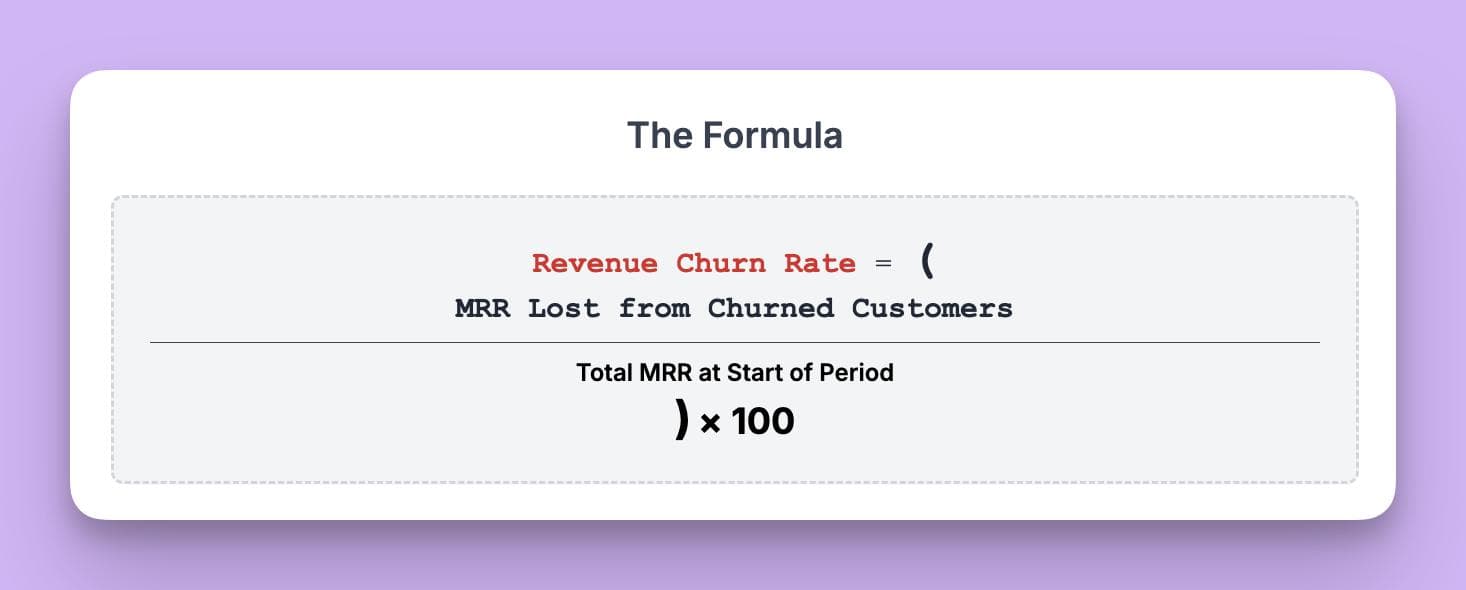
This metric helps subscription businesses understand the financial impact of losing customers, especially if those customers contribute varying amounts to monthly recurring revenue.
Common Calculation Mistakes
A frequent error is failing to account for new customers acquired during the period, which can distort churn calculations.
It's important to use the number of customers at the beginning of the period, not the average or end count, to maintain consistency.
Additionally, confusing customer churn rate with retention rate or mixing revenue churn with customer churn can lead to misinterpretation of data.
Customer Churn Benchmarks by Industry
Churn rates vary significantly depending on the industry, business model, and customer segments.
Industry-Specific Benchmarks
For B2B SaaS businesses, the average annual churn rate is 3.5% to 4.9%, with best-in-class companies maintaining rates under 5%.
Subscription-based e-commerce might experience higher churn due to competitive markets and lower switching costs.
What's a "Good" Churn Rate?
An acceptable churn rate depends on your industry and growth stage. Generally, a lower churn rate indicates better customer retention and loyalty.
For B2B companies, churn rates tend to be lower than in B2C due to longer customer lifecycles and higher switching costs.
B2B vs. B2C Comparison
B2B businesses often enjoy more stable customer bases with lower churn rates, thanks to contractual agreements and deeper customer relationships.
In contrast, B2C companies face higher churn due to more price-sensitive customers and greater competition.
Why Customer Churn Matters: Business Impact
Customer churn has far-reaching consequences beyond just losing customers.
Financial Impact
Losing customers directly reduces revenue and increases customer acquisition costs (CAC) as companies spend more to replace lost customers.
Additionally, churn shortens the average customer lifetime, reducing customer lifetime value (CLV) and jeopardizing sustainable growth.
Studies show that improving customer retention can boost profits by 25% to 95%, underscoring the financial importance of managing churn effectively.
Reducing churn by just 5% can lead to a significant increase in profits, making it a key focus for businesses aiming for long-term success.
Customer churn costs U.S. businesses a staggering $136 billion annually, highlighting the importance of effective retention strategies.
Operational Impact
High churn rates complicate forecasting and planning, making it difficult for teams to predict future revenue and allocate resources.
It can also negatively affect employee morale, as teams face constant pressure to replace lost customers instead of focusing on growth and innovation.
Main Causes of Customer Churn
Identifying why customers leave is crucial for developing effective retention strategies. Analyzing churn helps businesses identify why customers leave and take proactive steps to improve retention.
Product-Related Causes
If a product or service fails to meet customer expectations or lacks essential features, customers may seek alternatives. Continuous product optimization based on customer feedback helps address these pain points.
Technical problems like bugs, glitches, frequent downtime, or a lack of desired features can frustrate customers and drive them away, emphasizing the need for robust product development and maintenance.
Customer Experience Issues
Poor customer service, complicated onboarding, or a confusing customer journey can frustrate customers and lead to churn.
Delivering excellent customer service and seamless experiences is key to maintaining customer loyalty.
Pricing and Value Mismatch
Customers may churn if they perceive the product’s price as too high compared to the value received.
Flexible pricing plans and clear communication of benefits can mitigate this risk.
Poor Support and Communication
Slow or unhelpful responses to customer issues contribute significantly to churn. Providing omnichannel support and proactive engagement helps retain customers.
External Factors
Sometimes, factors outside a company’s control, such as economic downturns or changes in customer needs, can cause churn.
How to Identify At-Risk Customers
Early identification of at-risk customers allows businesses to intervene before they churn.
Early Warning Signs
Declining customer engagement, increased support tickets, or negative customer feedback are red flags. Monitoring these signals helps spot churn customers early.
RFM Analysis Basics
Recency, Frequency, and Monetary (RFM) analysis segments customers based on their purchasing behavior, helping to identify those at risk of leaving.
Companies leveraging AI for customer intelligence can predict churn risks with greater accuracy.
Customer Health Scores
Combining multiple data points into a health score provides a predictive churn model that highlights customers who may soon stop paying or reduce their engagement.
How to Reduce Customer Churn: Prevention Strategies
Reducing customer churn requires a comprehensive approach across the customer lifecycle. Improving customer experience can decrease churn by almost 15%, making it a critical area of focus for businesses aiming to retain their customer base.
1. Onboarding Excellence
Setting clear expectations early and guiding new users effectively through the product or service lays a foundation for satisfaction and loyalty.
A strong onboarding process sets the tone for customer relationships and decreases churn, ensuring that customers feel supported and confident in their decision to engage with the product or service.
2. Customer Success & Engagement
Proactive engagement programs and regular check-ins help maintain strong customer relationships and address issues before they lead to churn.
Companies that prioritize customer success see churn rates drop by 20%, demonstrating the value of investing in customer success initiatives.
3. Customer Service Excellence
Offering omnichannel support and ensuring fast, helpful responses enhances the customer experience and reduces frustration.
4. Product Optimization
Acting on customer feedback to improve the product or service ensures it continues to meet customer needs and expectations.
Additionally, investing in customer education empowers users and decreases the likelihood of churn, as informed customers are more likely to stay engaged and satisfied.
5. Communication & Value
Consistent, personalized communication reinforces the product’s value and keeps customers engaged.
Building customer loyalty reduces churn and increases overall profitability, making it a cornerstone of long-term business success.
6. Reduce Involuntary Churn
Managing failed payments through dunning processes and offering multiple payment options minimizes passive churn.
7. Pricing Flexibility
Providing upgrade or downgrade paths and pause options instead of outright cancellation helps retain customers facing changing needs.
Key Related Metrics
Tracking related metrics alongside churn rate offers a holistic view of customer health.
- Customer Retention Rate: The inverse of churn, indicating the percentage of customers retained.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total revenue expected from a customer over their lifetime.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): A key metric for subscription businesses reflecting predictable revenue.
- Customer Satisfaction and Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures of customer happiness and loyalty.
Reduce Customer Churn with InstantDocs Today
InstantDocs is an AI-powered knowledge base software designed to help businesses reduce customer churn by enhancing customer engagement and streamlining communication through efficient support documentation.
It enables teams to quickly create, maintain, and update help documentation automatically. This addresses common issues like time-consuming manual writing, outdated articles, and loss of valuable knowledge from resolved support tickets.
Key features of InstantDocs include:
- AI Recorder: A Chrome extension that records walkthrough videos of product processes, automatically generating detailed help docs with step-by-step instructions, snapshots, polished voiceovers, and synced video for professional-quality support content.
- Video Editor: A built-in tool to edit scripts, fix sync issues, customize intros/outros, and add on-screen elements, creating visually engaging help videos within documentation.
- Notion-like Editor & Knowledge Base: An intuitive editor allowing drag-and-drop editing and organization of docs into collections and sections. Users can build a branded, visually appealing central knowledge base with a customizable landing page.
- Knowledge Gap Detection: Automatically identifies missing or outdated documentation by analyzing support tickets. It highlights knowledge gaps with related ticket summaries, enabling auto-generation or updates of docs that can be reviewed and published quickly, with plans for full automation in the future.
- Integrations: Supports importing existing knowledge bases from platforms like Zendesk, Intercom, Confluence, Notion, Crisp, and Google Docs.
By leveraging InstantDocs, companies can improve customer success initiatives, collect valuable customer feedback through enhanced support, and identify at-risk customers early.
This leads to better customer retention, reduced churn rates, and sustainable revenue growth, making it an essential tool for managing customer churn effectively.
FAQs
1. What is customer churn?
Customer churn is the rate at which customers stop doing business with a company during a specific time period. It reflects how many customers leave and can be calculated as a percentage of the total customer base.
2. How do I calculate churn rate?
Calculate churn rate by dividing the number of customers lost during a period by the total customers at the start of that period, then multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
3. What causes customer churn?
Common causes include product issues, poor customer experience, pricing mismatches, inadequate support, and external factors like changing customer needs.
4. What's a good churn rate?
A good churn rate varies by industry but generally, lower rates indicate better retention. For SaaS businesses, monthly churn under 1% is often considered healthy.
5. How do I reduce customer churn?
Focus on excellent onboarding, proactive customer success, responsive support, product improvements, personalized communication, and managing involuntary churn.
6. Churn rate vs. retention rate?
Churn rate measures customers lost, while retention rate measures customers kept. They are complementary metrics.
7. How often should I measure churn?
Churn should be tracked regularly—monthly for subscription businesses—to quickly identify trends and act accordingly.
8. What's the impact on CLV?
High churn reduces customer lifetime value by shortening the duration customers stay and pay, limiting revenue growth potential.
We guarantee a 65% AI resolution rate in 90 days, or you pay nothing.
End-to-end support conversations resolved by an AI support agent that takes real actions, not just answers questions.